One Chemical, Many Standards: Navigating SDS Variations Worldwide
One Chemical, Many Standards: Navigating SDS Variations Worldwide
The safe use of chemicals is a universal concern — but how chemical safety information is communicated varies from country to country. The Safety Data Sheet (SDS) plays a central role in this communication. While the introduction of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) aimed to standardize these documents, significant regional differences remain in how SDSs are formatted, enforced, and localized.
- “Global Harmonization” is not always harmonized globally
The GHS, developed by the United Nations, provides a standardized 16-section format for SDSs. These sections cover everything from chemical identification and hazards to handling, storage, and regulatory information. However, the GHS is not legally binding; it must be adopted and enforced by national or regional authorities, each of which can choose which version to implement and how strictly to regulate it.
Here’s a few examples of certain countries and regions and their current SDS regulations:
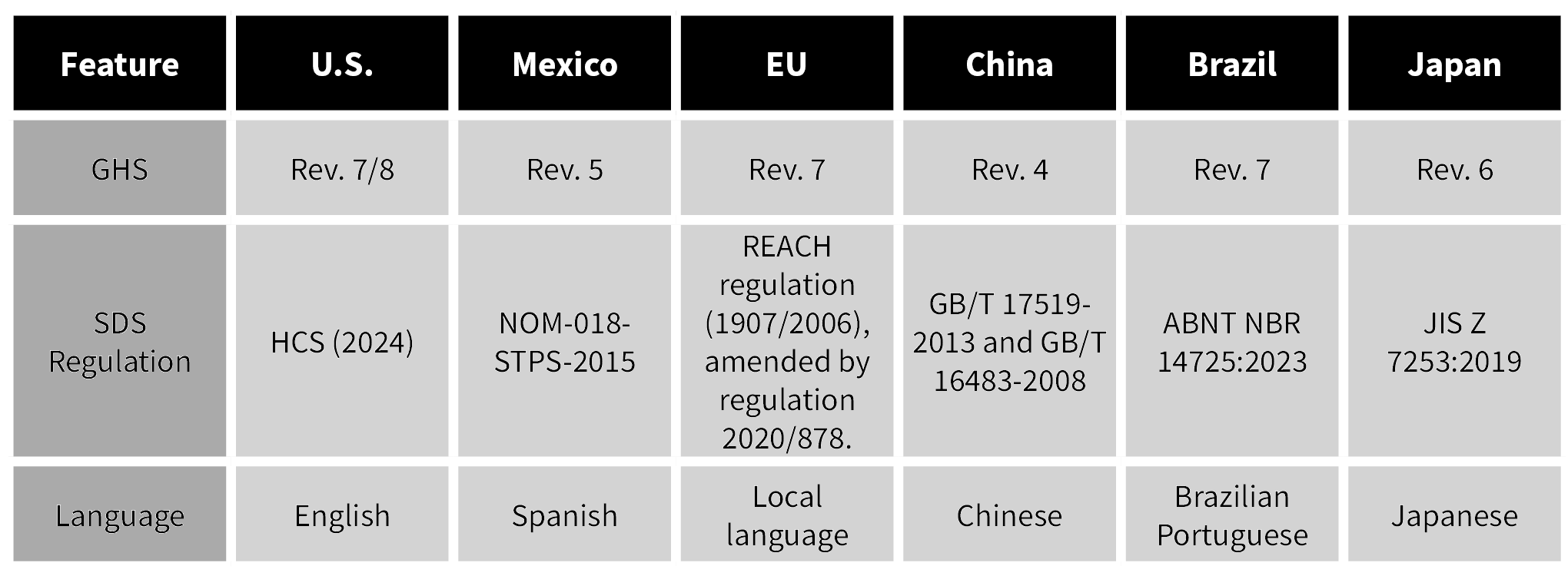
Differences in Classifications:
- Countries such as China, Japan, and Australia have implemented their own national adaptations of GHS with unique classification lists and compliance procedures.
- Supplemental statements are used within the European Union to provide additional information about hazards. For example, “EUH066: Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness or cracking”.
- United States has unique hazards such as combustible dust and simple asphyxiant.
Format and Section Enforcement
While most regions use the 16-section format, specific details are required throughout different sections of the SDS. For example:
- Section 1
- In the U.S., OSHA requires the Name, U.S. address and U.S. telephone number of the chemical manufacturer, importer or other responsible party to be listed in Section 1.
- China requires a domestic, 24-hour emergency number.
- In Europe, poison center numbers are required on Safety Data Sheets, in addition to emergency response numbers.
- Section 3
- US and Canada have prescribed concentration ranges that can be used to protect proprietary information.
- Section 8, 14, and 15: When available, country specific information is often required/ recommended to be displayed in these sections.
- US has OSHA permissible exposure limits and American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) Threshold Limit Values in Section 8
- Canada’s domestic Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) is listed in Section 14 on a Canadian SDS, whereas Road Transport of Dangerous Goods (RTDG) is listed on a Korean SDS.
- German Water Hazard Class (WGK) and other REACH specific lists will be displayed in Section 15 on a German SDS whereas the Japanese Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law will be listed on a Japanese SDS.
Update Frequency and Responsibility
- EU: SDS must be updated immediately when new hazard info is available.
- US: Must update SDS within 3 months of new information.
- Japan and China: Typically update with any regulatory change or new data.
The Importance of Local Compliance
For global manufacturers and chemical distributors, understanding these differences is crucial. A SDS compliant in the U.S. may fall short of requirements in Brazil or China. Having a compliant SDS is a matter of both safety and business continuity. Incorrect or incomplete SDS can lead to occupational hazards, workplace incidents as well as regulatory fines or supply chain delays.
Conclusion
The SDS is a universal tool for identifying important safety information, but its implementation is anything but uniform. Businesses operating across multiple regions must navigate a complex matrix of local laws, language requirements, and regulatory standards. While GHS has made great strides in harmonizing chemical safety communication, regional differences will continue to shape how SDSs are created, reviewed, and used around the world. Tailoring these documents to meet the specific requirements of each region will not only enhance the safety of all users handling your hazardous materials but also reinforce your commitment to global product stewardship.
How can CHEMTREC help?
CHEMTREC’s SDS Authoring Service, employs a team of dedicated SDS authors with an in-depth understanding of the regulatory landscape which will put your mind at ease with high quality, customized, cost-effective Safety Data Sheets. Our service includes regions throughout the world and over 50 different languages. Have peace of mind knowing your documents are up to date year after year with our ongoing maintenance program. Click here to receive a quote or learn more about this service along with CHEMTRECs other SDS suite of services.
Request a Quote for SDS Authoring
Interested in SDS Authoring? We work with companies of all sizes and create Safety Data Sheets in several languages. Complete a request and we'll be in touch soon!
Is Your SDS Portfolio Up-to-Date?
Check all that apply to your business:
We don’t have a centralized SDS library.
We don’t have digital access to SDSs.
Our SDSs aren’t accessible 24/7 to employees or responders.
New information has become available and our SDS needs to be updated.
We’re unsure if our SDSs meet GHS requirements.
We don’t have SDSs in local languages.
Employees don’t know where to find or how to use an SDS.
We’ve received audit findings or warnings related to SDS compliance.
Contact Our Sales Team
Interested in chatting right now? Email our team at sales@chemtrec.com or call us at 1-800-262-8200 Monday through Friday, 8:00am-5:30pm ET.